
Space images are always a subject of interest with a ‘wow factor’ that leave a tiny bit of wonder while looking down to our planet. These stunning images of space enables to view the galaxies and the space objects nearer and to view the gorgeous part of the space. Here is the top 10 list of stunning images of space that will leave your mouth open!

The image of Comet ISON is an image taken by NASA Hubble Space Telescope that reveals the subtle structure in the inner coma of the comet which decreases its brightness proportional to the distance from the nucleus. The comet’s coma appears cyan, a greenish-blue color due to gas, while the tail is reddish due to dust streaming off the nucleus. When photographed, the comet was inside Mars’ orbit and 177 million miles from Earth. However this information inadequate in determining the comet’s shape and evolution.

The image of the “wing” of the Small Magellanic Cloud galaxy from the NASA’s Great Observatories gives a dazzling view of a small galaxy about 200,000 light-years. The purple color shows the X-rays from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory; red, green and blue shows the presence of visible-light from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and infrared observations from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope are also represented in red. This bright galaxy closest to the Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye from the Southern Hemisphere and near the equator.
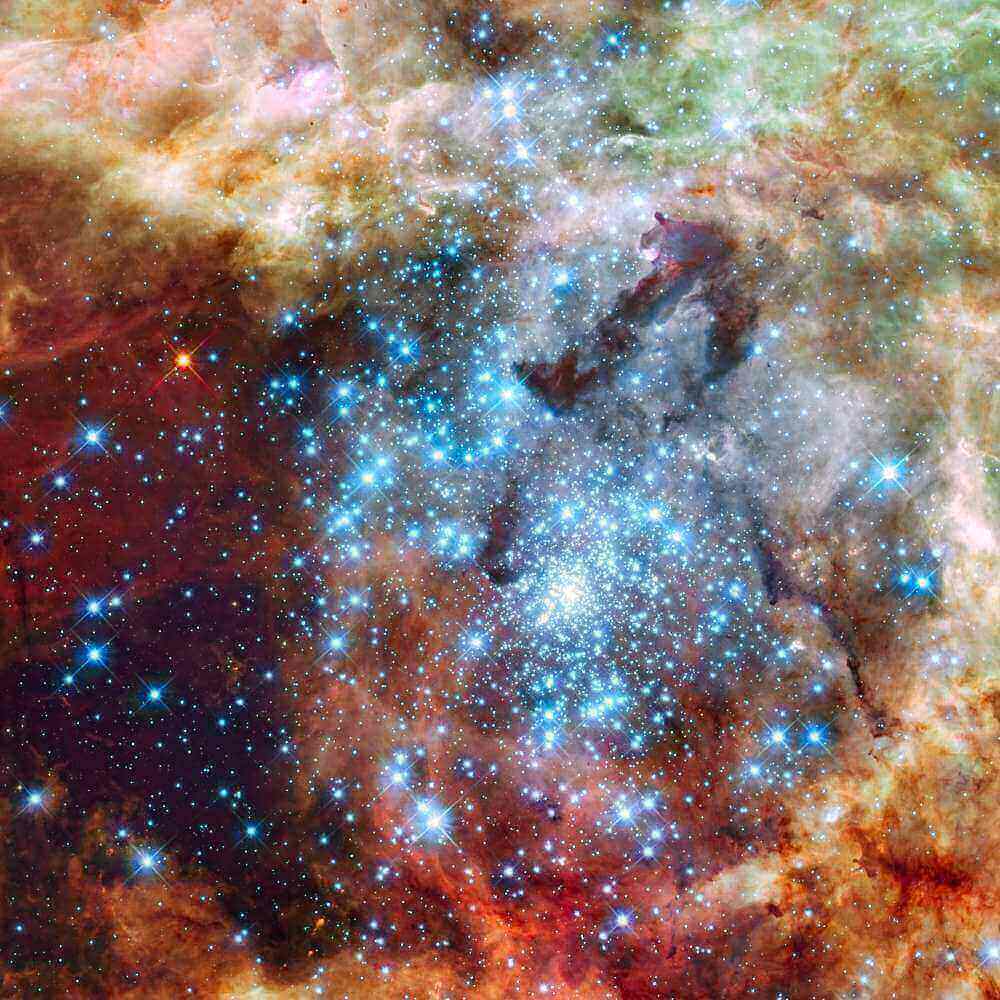
The image of the merging clusters in the gigantic 30 Doradus Nebula, which is 170,000 light-years from Earth is believed to be the picture of star clusters in the early stages of merging. In this Hubble space telescopic image, the green shows the glow of oxygen; the blue color light from the hottest, most massive stars and the red from fluorescing hydrogen.

The Hubble Space Telescope has imaged the planetary nebula that contains the outer layers of a star that were expelled into interstellar space which lies in the southern constellation of Pyxis (the Compass). The glowing gaseous shrouds in the nebula were shed by the central star to sustain the nuclear reactions in its core and may fade gradually over tens of thousands of years. The colors in the image represent a range of emissions coming from the clouds of the nebula where the red represents nitrogen, green represents hydrogen, and blue represents oxygen.

The Hubble telescope imaged a turbulent star-birth region in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way that resides in the 30 Doradus Nebula. Many of the diamond-like icy blue stars that are 100 times more massive than our sun often pop off like firecrackers. The nebula is close enough to Earth that Hubble can resolve individual stars and provide astronomers important information about the stars birth and evolution. The blue color is light from the hottest, most massive stars; the green from the glow of oxygen; the red from fluorescing hydrogen.

The image captured by the NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory clearly gives a view on sun emitting a mid-level flare. These powerful bursts of radiation are powerful enough to disturb the atmospheric layer where GPS and communications signals travel, but may not be intense enough to cause physical harm to humans on the ground.

The NPP satellite with the help of VIIRS instrument gathered enough pixels to form this synthesized view of Earth showing the Arctic, Europe, and Asia. The satellite orbits the Earth about 14 times each day and observes nearly the entire surface and records all critical information for climate change science.

This is the best infrared image that shows the star-studded center of the Milky Way towards the constellation of Sagittarius. These infrared observations make numerous complex and mysterious objects present in the galaxy visible which were usually hidden at optical wavelengths by clouds of dust. It is possible to see stars spinning around the supermassive black hole located right in the center of the image even though the main cosmic object still remains invisible.

The image shows the remnants of a white dwarf star exploded violently as a supernova around 600 years ago and is visibly seen as thin blood-red shells. These delicate gas make up is located over 150 000 light-years from Earth, present in the southern constellation of Dorado, a constellation that also contains the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) galaxy.

This best ever image of the Antennae Galaxies snapped by NASA’s Hubble space telescope shows a pair of galaxies. Clouds of gas are seen in bright pink and red which is surrounded by the bright flashes of blue star-forming regions which are partially obscured by dark patches of dust. The Antennae Galaxies are said to be in a state of starburst, a period in which all of the gas within the galaxies is being used to form stars